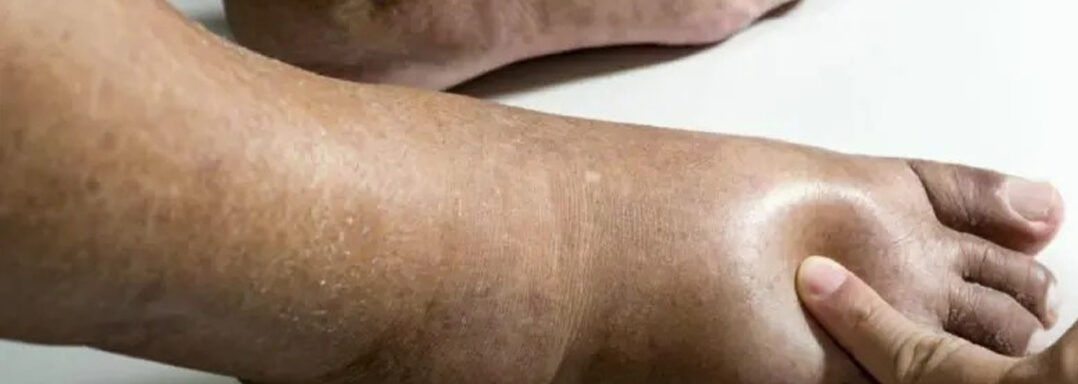
Leg swelling from standing is not caused directly by high blood pressure. Untreated hypertension can cause cardiovascular issues that can cause edema.
Other factors may also cause the effects of prolonged standing. To effectively manage leg swelling, underlying hypertension and lifestyle factors must be addressed.
High blood pressure can cause fluid retention, swelling of the legs, and even kidney failure because of impaired kidney function.
It can also affect the eyes, resulting in vision loss. High blood pressure can lead to leg pain when walking, cold feet, or a stroke if it affects circulation.
This blog post will explore the ins and outs of high blood pressure and leg swelling and their association with cycling. We’ll also share some enlightening tips to help you manage high blood pressure and prevent leg swelling while cycling, contributing to a healthier, more comfortable ride.
- Hypertension can contribute to leg swelling, with causes ranging from kidney failure, cardiomyopathy, chronic kidney disease, heart failure, obesity, prescription medications, and damaged blood vessels.
- Factors that can increase leg swelling when cycling with high blood pressure include the intensity and duration of exercise, hydration and electrolyte balance, certain medications, underlying health conditions, heat exposure, body position, and post-exercise blood pressure drop.
- Managing high blood pressure is essential to reduce leg swelling during cycling. Tips for controlling blood pressure include a slow warm-up and cool-down, regular exercise, a healthy diet, proper hydration, stress management, adequate sleep, medication compliance, and regular consultation with healthcare professionals.
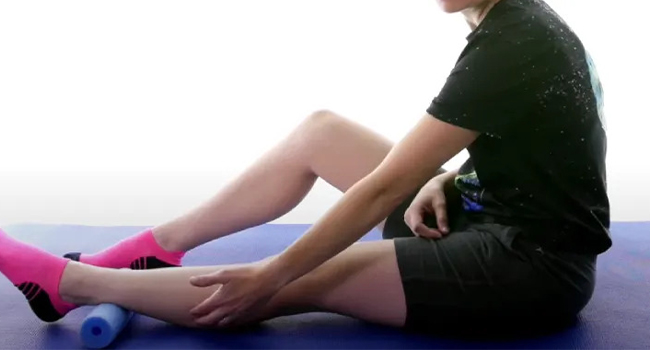
- Several techniques can ease leg swelling caused by cycling, such as avoiding prolonged standing or sitting, elevating feet, staying active, massaging feet and legs, soaking legs in Epsom salts, and using compression socks.
- Cycling can benefit cardiovascular health. However, controlling high blood pressure during rides is crucial, particularly for those experiencing leg swelling. The right approach, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, proper hydration, and stress management, can help manage hypertension and leg swelling.
Can High Blood Pressure Cause Leg Swelling Due to Cycling: 7 Effects
A hypertensive state involves elevated pressure within the arteries, which can result in several health complications. Multiple factors can contribute to leg swelling associated with hypertension. Some common causes of leg swelling in people with high blood pressure include:
- Acute Kidney Failure: Dysfunction in the kidneys disrupts fluid balance, causing fluid retention and subsequent swelling, particularly in the legs.
- Cardiomyopathy: This condition affects the heart muscle’s pumping capacity and can cause fluid buildup in various body parts, including the legs.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Similar to acute kidney failure, chronic kidney disease can impair the kidneys’ ability to regulate fluid levels, contributing to edema.
- Heart Failure: Blood doesn’t get pumped efficiently, fluid accumulates in the legs and other body parts, causing swelling.
- Obesity: Weight gain strains the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of hypertension and subsequent leg swelling because of fluid retention.
- Prescription Medications: Certain medications used to manage high blood pressure or other health conditions may have side effects, including edema as a potential complication.
- Damaged Blood Vessels: Over time, uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage blood vessels, impairing their ability to effectively regulate fluid movement and leading to leg swelling.
High Blood Pressure May Increase the Risk of Leg Swelling When Cycling
Leg swelling, also known as edema, can occur because of various factors, especially in cycling with high blood pressure. Here are some factors that may increase the likelihood of experiencing leg swelling:
- Intensity of Exercise: Blood pressure naturally rises during physical activity. If the cycling intensity is too high, it may increase blood pressure that might contribute to swelling in the legs.
- Duration of Cycling: Prolonged cycling periods without adequate breaks can lead to fluid accumulation in the legs, resulting in swelling and a higher risk of leg loss.
- Hydration and Electrolyte Balance: Drinking excessive water without replenishing electrolytes can lead to hyponatremia, which can cause edema. Conversely, not drinking enough can lead to dehydration, affecting blood pressure and potentially contributing to swelling.
- Medications: Some blood pressure medications can cause leg swelling as a side effect. Talking to your doctor about the medicines being taken and their potential side effects is important.
- Underlying Health Conditions: High blood pressure can be a sign of more severe conditions such as heart failure or kidney disease, which can also cause edema.
- Heat Exposure: Cycling in hot weather can cause vasodilation and more blood flowing to the skin, which may cause swelling.
- Body Position: Sitting while cycling can contribute to poor leg circulation, leading to swelling, especially if the bike setup is not ergonomically optimized.
- Post-Exercise Blood Pressure Drop: A drop in blood pressure after stopping exercise can cause blood to pool in the legs, leading to swelling.
Management and Prevention Tips High Blood Pressure Causes Leg Swelling Due Cycling
Managing high blood pressure is crucial for reducing the risk of leg swelling during cycling. Here are some tips to help you manage your blood pressure while enjoying your rides.
Gradual Warm-Up and Cool-Down
Starting with a gentle warm-up and ending with a cool-down is essential to ensure a safe and effective workout. These practices help your blood vessels adjust gradually to the changes in blood flow and pressure, reducing the risk of injury and cycling-induced leg swelling and promoting overall cardiovascular health. So, take the time to prepare and recover your body before and after exercise.
Regular Exercise
Cycling regularly can have numerous benefits for your heart health, including lowering blood pressure and strengthening the heart muscle. However, it’s crucial to pace yourself to prevent excessive leg swelling. Over time, sensible and regular cycling can lead to a more efficient cardiovascular system and a reduced risk of heart disease.
Healthy Diet
Maintaining a healthy diet can support your cycling routine and help manage leg swelling. Healthy foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limiting salt intake can also help control blood pressure and reduce leg swelling, which is crucial for a healthy cardiovascular system.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial when cycling, and drinking plenty of water before, during, and after your ride can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels and prevent leg swelling. Water is an essential nutrient that keeps your body functioning properly and replenishes fluids lost during exercise, key to avoiding dehydration and maintaining energy for your rides.
Stress Management
Relaxation techniques like deep breathing keep your blood pressure in check. These simple exercises can help you stay calm and centered, even during a hectic day. With regular practice, you may find that your stress levels decrease, your blood pressure stays within a healthy range, and cycling-induced leg swelling can be kept to a minimum.
Adequate Sleep
Getting enough quality sleep is crucial for maintaining good overall health and managing conditions like leg swelling. Poor sleep can negatively impact blood pressure, leading to various health problems. Prioritize getting the recommended amount of sleep each night and take steps to improve the quality of your sleep.
Medication Compliance
If you have been prescribed blood pressure medication or medication to manage leg swelling, it is vital to take it as directed by your healthcare provider. Skipping your doses or not taking your medicine as directed can increase your risk of complications. Discuss any concerns or questions about your medicines with your healthcare provider.
Consult Healthcare Professionals
Monitoring your blood pressure levels and adjusting your cycling routine is essential. Doctors can help you effectively manage conditions like leg swelling and blood pressure. Then you can make informed choices about your fitness regimen and overall well-being.
Other ways to ease leg swelling caused by high blood pressure
- Avoid Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Keep movement regular to prevent fluid accumulation.
- Elevate Your Feet: Enhance circulation by elevating your leg above heart level.
- Stay Active: Walking around helps maintain fluid circulation in your legs.
- Opt for Massage: Help circulate blood flow by massaging your feet and legs.
- Epsom Salt Soak: Reduce swelling by soaking legs in Epsom salts.
- Compression Socks: Prevent fluid buildup with compression socks.
Conclusion
Cycling is an excellent cardiovascular workout, but managing high blood pressure during your rides is crucial to the healthy equation, especially if you’re grappling with leg swelling. It’s Many things contribute to this condition, from the intensity of your exercise to your hydration levels and even your medications.
However, the good news is that you can manage hypertension and leg swelling maze with proper management through a balanced diet, regular exercise, hydration, and stress management.
Always remember the power of a good warm-up and cool-down. Also, remember the benefits of staying active, massaging your legs, and using compression socks.
Remember, while cycling can initially be an uphill ride when dealing with hypertension, with the right approach, it can turn into a scenic journey towards better health.
FAQs
What Is The Normal Heart Rate When Cycling?
Cyclers tend to achieve their target heart rates for exercise faster during their ride, even though bikes do not record target heart rates. Exercise should be performed at a heart rate between 80 and 150 beats per minute for people between 45 and 60. Aim for 75-136 beats per minute for those 65 and older.
How To Take Blood Pressure On Leg?
Wear loose-fitting clothes. Place the blood pressure cuff around your thigh, calf, or ankle on the appropriate part. Use the same leg regardless of which leg you use. Using the ankle may be less painful than using the calf.