Fever disrupts the body’s ability to regulate temperature, which makes cycling uncomfortable and increases the risk of heat-related issues. Cycling while experiencing a fever also weakens the immune system, potentially prolonging illness and recovery. Additionally, fever can lead to fatigue and weakness, impairing a cyclist’s ability to maintain their usual level of performance.
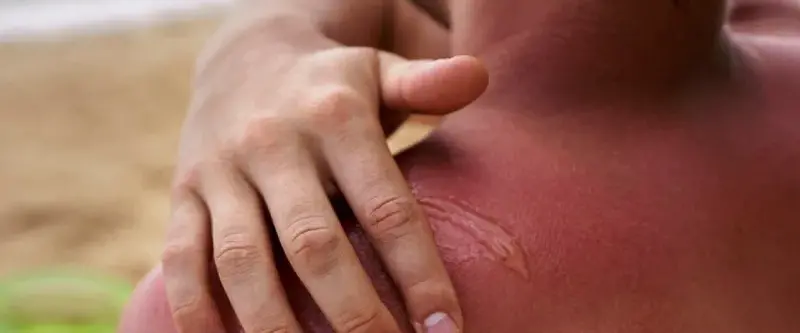
Sunburn itself doesn’t directly cause fever, but severe sunburn leads to a systemic inflammatory response that might cause a fever.
When you have a sunburn, your body may react similarly to an infection, which might lead to a fever. This can often resemble flu symptoms or an allergic reaction, such as shivering in bed, headaches, fever, and chills.
In this post, we’ll explore why sunburn can trigger a fever and what that means for cyclists. From understanding your body’s inflammatory response to managing the effects on your performance, we’ve covered you with the essential information to stay calm and ride strong.
Can Sunburn Cause Fever For Cycling: 9 Reasons

Cyclists spend significant time outdoors, exposing themselves to various environmental factors. One common issue they face is sunburn, which can lead to a fever. Understanding why sunburn causes fever involves exploring how the body reacts to excessive sun exposure and the associated mechanisms that trigger this response.
Body’s Inflammatory Response
If the skin is exposed to UV radiation, it causes damage at the cellular level. This damage activates the body’s inflammatory response, which attempts to repair the injured tissue. The inflammatory process involves several key steps:
- Inflammatory Mediators Release: When UV radiation damages skin cells, they release inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandins and cytokines. These substances signal the immune system to initiate an inflammatory response.
- Increased Blood Flow: To deliver immune cells and nutrients to the damaged area, blood vessels in the affected skin dilate. This increased blood flow contributes to the redness and warmth characteristic of sunburn.
- Immune Cell Activation: Immune cells, including white blood cells, migrate to the injury site to help repair the damaged tissue. This response can cause swelling and tenderness in the affected area.
Fever as a Systemic Response
Fever is a systemic response to inflammation and infection. When the body experiences significant inflammation, such as from severe sunburn, it can increase body temperature. Here’s how:
- Cytokine Release: The inflammatory mediators released during sunburn include cytokines, proteins that play a crucial role in the immune response. Some cytokines, such as interleukins, can affect body temperature by affecting the hypothalamus.
- Hypothalamic Response: When the hypothalamus detects these cytokines, it raises the body’s set point temperature, which we recognize as fever. The body aims to create an environment less favorable for pathogens and enhance the immune response.
- Systemic Effects: Severe sunburn can cause widespread inflammation, which affects the entire body, not just the skin. This systemic inflammation can trigger fever as the body attempts to combat the widespread inflammatory response.
Cyclists and Sunburn-Induced Fever
Cyclists are at a higher risk of sunburn because of prolonged exposure to sunlight during rides. Several factors contribute to this risk:
- Extended Sun Exposure: Long rides increase the likelihood of sunburn, especially if cyclists must be more diligent about applying sunscreen or wearing protective clothing.
- High Altitude: Cycling at higher altitudes can intensify UV radiation exposure, increasing the risk of sunburn and subsequent fever.
- Intense Physical Activity: Physical exertion increases blood flow and body temperature, which can exacerbate the effects of sunburn and contribute to a higher risk of fever.
5 Effects of Fever on Cyclists Because of Sunburn

Cyclists often face intense sun exposure, especially during long rides or races. While sunburn is a common issue, it can sometimes lead to more severe health concerns, such as fever. This increase in body temperature can significantly affect a cyclist’s performance and overall well-being. Understanding the impact of sunburn fever on cycling performance and taking appropriate measures to manage it is crucial.
Reduced Performance
- Decreased Endurance: Fever increases your body’s core temperature, leading to early fatigue and reduced stamina. Cyclists may need help maintaining their usual pace or completing their rides.
- Impaired Coordination: Elevated body temperature and discomfort from fever can affect motor skills and coordination, making it harder to handle the bike safely and efficiently.
Increased Dehydration
- Excessive Sweating: Fever often causes excessive sweating as the body tries to cool down. This can lead to significant fluid loss for cyclists, increasing the risk of dehydration.
- Electrolyte Imbalance: Along with water, sweating depletes essential electrolytes crucial for muscle function and overall health. A muscle imbalance can result in cramping and weakness.
Heat-Related Illnesses
- Heat Exhaustion: Extreme heat and fever can cause heat exhaustion, manifesting as dizziness, headache, and nausea. Cyclists experiencing these symptoms may need to stop and seek shade or hydration immediately.
- Heatstroke: In severe cases, sunburn and fever can escalate to heatstroke, a life-threatening condition requiring urgent medical attention. Symptoms include confusion, rapid pulse, and loss of consciousness.
Delayed Recovery
- Longer Healing Time: Sunburn-induced fever can prolong the healing process for sunburned skin. This extended recovery time can interfere with training schedules and overall fitness goals.
- Increased Sensitivity: Recovering from sunburn and fever might leave the skin more sensitive to further sun exposure, increasing the risk of subsequent burns and related issues.
Compromised Immune Function
- Immune Response: A fever indicates that the body’s immune system is working hard to combat the damage from sunburn. Cyclists might experience a temporary decrease in immune function, making them more susceptible to other illnesses or infections.
Management Of Fever-Induced Effects

To minimize the impact of fever on cycling performance, cyclists should:
- Stay Hydrated: Increase fluid intake and take electrolyte supplements to counteract dehydration.
- Rest and Recover: Allow time for the body to heal from sunburn and fever. Avoid intense training until symptoms subside.
- Use Cooling Methods: Apply cool compresses and soak in lukewarm water to ease discomfort.
- Seek Medical Attention: If fever symptoms persist or worsen, consult a healthcare professional for treatment.
Conclusion
Sunburn might seem like a pesky inconvenience, but it can seriously impact your cycling performance when it leads to fever. From reducing endurance and causing dehydration to increasing the risk of heat-related illnesses, the effects of fever can take a toll on your ride.
By staying hydrated, using cooling methods, and taking time to recover, you can better manage the challenges of sunburn-induced fever. Remember these tips to keep those wheels turning smoothly.
Remember, a little prevention and care can go a long way in ensuring your rides remain enjoyable and injury-free.
FAQs
Is It Normal To Have A Fever After Sunburn?
Red, tender, or sensitive skin are possible symptoms of sunburn. Blistering that develops hours or days later. Symptoms include fever, chills, nausea, and rash (known as “sun poisoning”).
When Do I Get A Fever After Burning?
The median time to first fever was 16 hours post-burn injury. Patients developed fever regardless of burn type (scald, flame, flame, and inhalation or contact), and depth of burn.