Swelling from sunburn causes significant pain and discomfort for cyclists, making it hard to pedal and maintain bike control. The stiffness and reduced mobility in sunburned areas hinder performance and affect overall ride efficiency. Increased fluid loss due to sunburn raises the risk of dehydration, which can further exacerbate swelling and fatigue.
Yes, sunburn can cause swelling, especially in the exposed areas of your skin. When you get sunburned, blood vessels dilate to increase blood flow, and immune cells rush to the affected skin to aid recovery, leading to swelling.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the science behind why sunburn can lead to swelling and how it can disrupt your cycling experience. So buckle up, and let’s ride through this enlightening journey together.
Can Sunburn Cause Swelling For Cycling: 8 Reasons
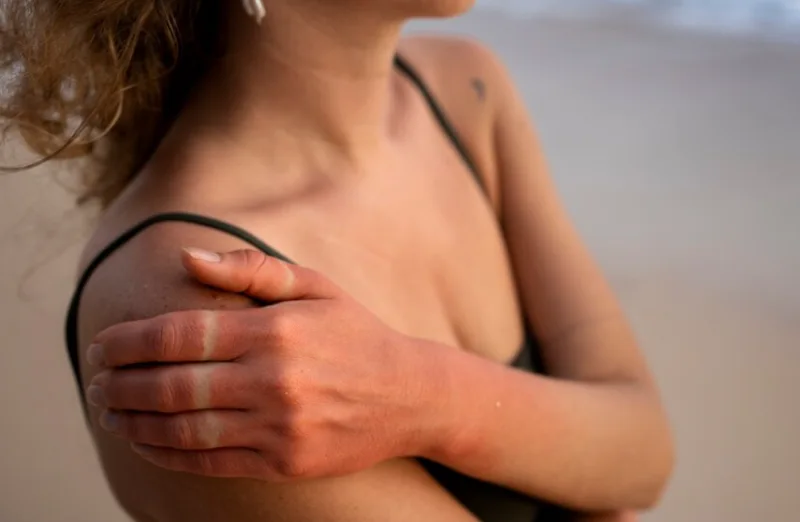

Cycling under the sun can bring about many challenges, including sunburn. Beyond the familiar discomfort and redness, sunburn can also cause swelling, further disrupting your cycling experience. If you are aware of the reasons behind why this occurs, you can manage the symptoms more effectively and get back to enjoying your rides. Here are the key reasons for sunburn leading to swelling, particularly relevant for cyclists:
Inflammatory Response
When your skin is exposed to ultraviolet rays, it triggers an inflammatory response. This is the body’s natural defense mechanism to repair and protect damaged tissues. The inflammatory process involves dilating blood vessels in the affected area to increase blood flow.
This increased blood flow brings immune cells to the injury site to help heal. However, this process can also cause swelling, as the enlarged blood vessels and the accumulation of immune cells lead to fluid leakage into the surrounding tissues.
- Immune cells are directed to the damaged area.
- Swelling results from fluid accumulation and increased blood flow.
Fluid Leakage
Sunburn damages the skin cells, causing them to break down and leak fluid. This fluid accumulates in the tissues surrounding the sunburned area, leading to swelling, also known as edema.
The severity of this fluid leakage can vary depending on the extent of the sunburn. For cyclists, the swelling can be particularly noticeable in areas frequently exposed to the sun, such as the arms, legs, and neck.
- Damaged skin cells leak fluid.
- Fluid accumulation causes swelling.
- Swelling is more noticeable in frequently exposed areas.
Water Retention
Cyclists often experience water retention in their feet and ankles due to prolonged periods of sitting or standing during rides. Sunburn can exacerbate this condition, making the swelling more pronounced. The body’s response to sunburn can further impair fluid balance, leading to increased water retention and more noticeable swelling in areas affected by sunburn.
- Prolonged sitting or standing can cause water retention.
- Sunburn can worsen water retention.
- Increased swelling may occur in affected areas.
Heat and Sun Exposure
Continuous exposure to heat and UV rays while cycling can intensify the effects of sunburn. The combination of direct sun exposure and physical exertion increases the likelihood of severe sunburn and associated swelling.
Heat can exacerbate the inflammatory response, leading to more pronounced swelling as the skin struggles to cope with both sunburn and elevated temperatures.
- Prolonged sun and heat exposure can worsen sunburn.
- Increased heat can intensify swelling.
- The body’s response to sunburn is heightened by physical exertion.
Increased Blood Flow
To aid in healing, the body increases blood flow to the sunburned area. This increased circulation helps repair damaged tissues but can also cause swelling as more blood and fluids are directed to the affected area. For cyclists, this means that areas like the arms and legs, which are more exposed to the sun, may swell significantly, especially after long rides.
- Increased blood flow aids in tissue repair.
- More blood and fluids reach the sunburned area.
- Swelling can be more pronounced in frequently exposed areas.
Compromised Skin Barrier

Sunburn compromises the skin barrier, making it more susceptible to swelling. Moisture retention and protection of the skin against external elements is weakened, leading to increased fluid leakage and swelling. For cyclists, sunburn can have a more significant impact, as the skin cannot effectively protect itself from further damage or fluid loss.
- Sunburn weakens the skin barrier.
- Compromised skin is more prone to fluid leakage.
- Increased swelling results from reduced skin protection.
Sensitivity and Allergic Reactions
Some cyclists may experience heightened sensitivity or allergic reactions to sunburn. This can further contribute to swelling, as the body’s response to UV damage may include allergic reactions that exacerbate inflammation and fluid accumulation. Sensitivity to the sun’s rays can vary from person to person, and those with heightened sensitivity may experience more severe swelling.
- Sunburn can trigger allergic reactions.
- Sensitivity to UV rays can worsen swelling.
- Individual responses to sunburn vary.
Tissue Damage
Severe sunburn can cause significant tissue damage, leading to increased swelling. The extent of damage to the skin and underlying tissues affects how much swelling occurs. For cyclists, especially those who spend long hours outdoors, the risk of severe sunburn and tissue damage is higher, potentially leading to more pronounced swelling in affected areas.
- Severe sunburn causes extensive tissue damage.
- Tissue damage leads to increased swelling.
- Long hours in the sun can heighten the risk of severe sunburn.
5 Effects of Swelling from Sunburn in Cycling
Swelling from sunburn can significantly disrupt your cycling experience. If you are aware of these effects, you can manage your condition better and mitigate the impact on your performance and comfort. Here are the key effects of sunburn-induced swelling on cycling:
Pain and Discomfort
One of the most immediate effects of swelling from sunburn is increased pain and discomfort. Sunburn can cause your skin to become extremely sensitive and tender. The swelling can exacerbate this pain, making it uncomfortable to continue cycling.
Friction from clothing and the pressure of sitting on the bike can aggravate the discomfort, making each pedal stroke or movement painful. This can detract from your overall cycling experience and may even force you to cut your ride short.
- Sunburn increases pain and sensitivity.
- Swelling exacerbates discomfort from friction and pressure.
- Pain can make cycling less enjoyable and challenging.
Reduced Mobility
Swelling can lead to stiffness and reduced mobility in the affected areas. If sunburn is on your legs or arms, you may find it difficult to move or stretch those limbs effectively. This stiffness can hinder your ability to pedal efficiently and maintain bike control.
Reduced mobility affects your performance and can lead to compensatory movements that might strain other parts of your body, potentially causing additional discomfort or injuries.
- The swelling reduces mobility and stiffness.
- Affected limbs may struggle with pedaling and bike control.
- Reduced mobility can impact overall cycling performance.
Increased Risk of Dehydration
Sunburn causes fluid loss through damaged skin, increasing your risk of dehydration. Maintaining hydration is crucial When cycling, especially under the sun. Dehydration can exacerbate swelling and make it more difficult for your body to recover.
It can also impair your performance, leading to reduced endurance and increased fatigue. Ensuring adequate hydration before, during, and after your ride is essential to manage swelling and maintain optimal performance.
- Sunburn-induced fluid loss increases dehydration risk.
- Dehydration can worsen swelling and performance.
- Staying hydrated is crucial for managing sunburn effects.
Delayed Healing
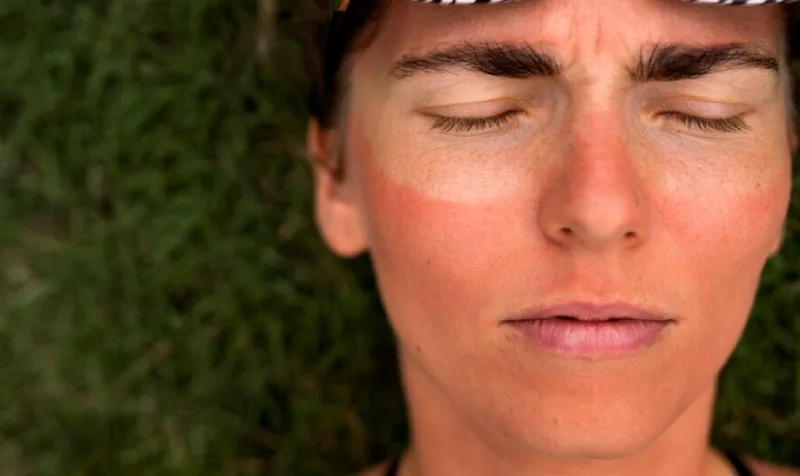

Continuous exposure to the sun and physical exertion can delay the healing process of sunburn. When you’re cycling while sunburned, the additional stress on your body can prolong the period of discomfort and swelling.
This delay in healing can lead to a longer recovery time, impacting your ability to cycle comfortably in the days following the sunburn. Taking steps to protect your skin and allow it to heal properly is vital for a quicker recovery.
- Physical exertion and sun exposure delay healing.
- Prolonged discomfort and swelling can affect recovery time.
- Proper skin care and rest are essential for faster healing.
Potential for Infection
Severe sunburn can compromise the skin barrier, increasing the risk of infection. The damaged skin is more vulnerable to bacteria and dirt, so you can get infections if you continue to cycle in unsanitary conditions.
Infections can exacerbate swelling and cause additional complications, making it essential to monitor the affected area closely and seek medical help if needed. Keeping the skin clean and protected is crucial to prevent infections.
Conclusion
To wrap things up, sunburn and subsequent swelling can indeed pose a significant challenge for cyclists. What at first might seem like slight discomfort can quickly escalate, impacting mobility, hydration levels, and healing process and potentially leading to infection.
Recognizing the potential effects of this issue is key, but remember, prevention is always the best cure. So, arm yourself with good sunscreen, hydrate regularly, and rest well to give your skin time to heal. After all, the sun shouldn’t dampen your spirit for cycling; it should fuel it.
FAQs
How Long Does Burn Swelling Last?
It is common for swelling to occur immediately after injury, and it usually subsides within 48 to 72 hours, although it can vary. Swelling will differ depending on the cause and location of the burn, as well as the depth and extent of the burn. As soon as possible, the swelling must be reduced.